Table of Contents
A Short Guide to GSM Technology
GSM technology is a widely used network for mobile communication all over the world. It was mostly preferred for its accessibility and affordability.
Handling GSM technology is simple and is still used in many other applications. Also, it is about to change in the coming years.
If you talk about history, in brief, the GSM (Global System for Mobile Communication) technology; generally called 2G is a digital technology used to transfer phone calls and information. The 4G module is very fast and it could transmit nearly 1 GB per second. Besides, today’s 5G network could make more than a Gigabyte per second. The usage of 2G in mobile communications is reduced because of its upgraded successors.
But, this is to remember that the GST network is the first and most affordable service that has digitized the world. Also, it ruled the digital world for years till technology reached an upgrade.
And, 2G is comparatively slower than its successors in speed and security. But today, 2G is mostly used in the Internet of Things (IoT).
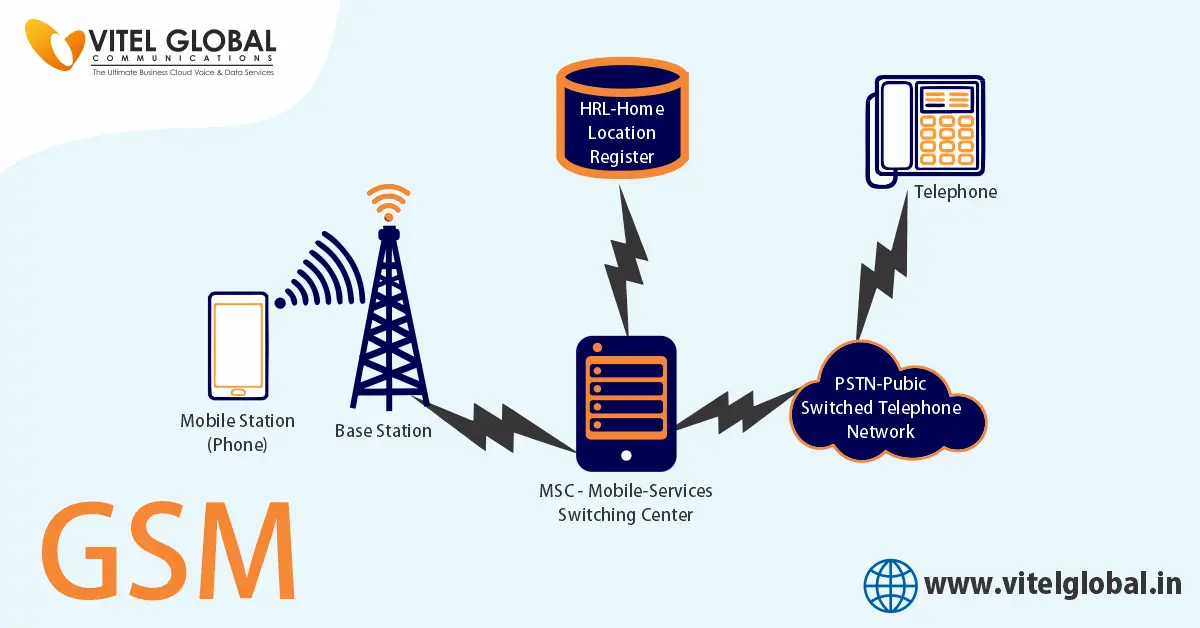
GSM Network Structure:
The 2G network works in 4 different stages namely;
- Mobile station
- BSS or Base Station Subsystem
- NSS or Network and Switching Subsystem and
- OSS or Operations Support System
Factually, it is important to understand that every network provider has its own network infrastructure. Every element above in turn has many components working together. Let’s go with each part of the network in brief.
Mobile Station:
In order to connect between each of the stages, the mobile station is the first stage where the user connects to the second one. For this to address, it is a device with a unique identity called Subscriber Identity Module (SIM). This SIM, in association with the device, connects the device to the 2nd stage – BSS.
Base Station Subsystem (BSS):
This is a combination of Base Station Controller and Base Transceiver Stations. The transceiver station contains the transmitter (antenna) and receiver.
Through this, the station is able to send and receive signals. The base station controller makes the base transceiver station stay intact with the signals that are through the network.
Network and Switching Subsystem (NSS):
It has many different components generally called Core Network/ Core System. This enables the voice calls with other components which include;
Mobile Switching Center (MSC) – Works as a standard switching node like authentication and registration
Home Location Register (HLR) – Includes the administrative information like the previously identified location
Visitor Location Register (VLR) – Includes selected data received from HLR
Equipment Identity Register (EIR) – This is a decision box that assesses if the device to permit over the network
SMS Gateway (SMS – G) – This works for Short message services
Authentication Center (AuC) – It contains the secret key related to the SIM card
Gateway Mobile Switching Center – Used to route the call
Operation Support System (OSS):
This is a cluster of many processes as well as technology with data and its application. The users manage their network with the help of OSS. Describing its usage, Operation Support System,
- Configures network components
- Manages offered services to the optimal level
- Keeping the system state intact and handling its errors
- Maintains service quality and the quality of experience
However, at the foundational level, all the network providers have the same infrastructure but to customize, additional features might be added to enhance the security and quality as well.
GSM Features:
Note, that the features of GSM technology cannot outrun today’s 5G tech. 2G systems consist of basic but essential and secure features. It is not an exaggeration to state that the security incorporated with the GSM system makes it the safest telecom standard available at its time. The features of the GSM module include:
- International roaming
- Compatible with ISDN (Integrated Service Digital Network)
- Phone book
- Alarms and Clock
- Allows new services
- Fixed dialing number
- Spectrum efficiency
- Short message service
- Encrypted phone calls
Conclusion:
In simple terms, to present the GSM module is safe and used by many sectors. GSM technology works for automation and security purposes. This is also used in medical services such as basic and simple telemedicine systems.
The limitation of the GSM technology is the bandwidth. It allows many users to use the same bandwidth and such a situation might give rise to random interference. Bandwidth limitation is the result of this. Apart from this, electronic interference is another drawback of the GSM module. Only, for this reason, it is necessary to switch off your mobile phones at places like airports and hospitals.
Grow your business and 𝒎𝒂𝒙𝒊𝒎𝒊𝒛𝒆 𝒑𝒓𝒐𝒅𝒖𝒄𝒕𝒊𝒗𝒊𝒕𝒚 with the industry’s best business communication service.
For more details, visit our website and start creating wonders in your organization right away.
For More Info or Book, Your Free Demo Today click here.